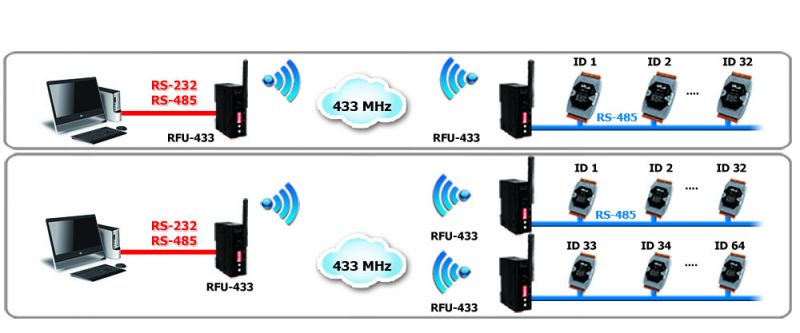
A wireless modem is a type of radio converter that is able to convert information that exists on a wired network, such as one connected using an RS-232 or RS-485 interface, etc., to a wireless network. The wireless modem is designed for data acquisition and control applications between a host and any remote sensors that are connected to the network. It is also useful for those applications where it is inconvenient or impractical to install physical cable wire. Not only can a wireless modem be used in peer-to-peer mode, but it can also be used in a multi-point structure.
|
|
||||||||
|
|
||||||||
| Model | Frequency | Transmission Distance (LoS) | External Antenna Base | External Antenna | Cable | Interface | Baud rate (bps) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RFU-400
|
429 MHz / 433 MHz | 1000 m | ANT-Base-01 (Note) |
- | 3S001-2 (1m) |
RS-232/485 | 1200~11520 | |
| RFU-433
|
433 MHz | 500 m | ANT-Base-02 (Note) |
- | 3S001-1 (1m) 3S003-1 (3m) |
|||
| RFU-433-RU400
|
433 MHz | 399 m | - | |||||
| SST-900B |
900 MHz | 700 m | - | |||||
| RFU-2400
|
2.4 GHz | 700 m | ANT-8 ANT-18 | 2400~11520 | ||||
| RFU-2400-RU400
|
2.4 GHz | 399 m | ANT-8 ANT-18 | |||||
| tRFU-2400
|
2.4 GHz | 180 m | - | - | - | RS-232/422/485 | ||
| Note: Magnetic Disk Base with 1.5m cable | ||||||||


